According to a recent study, simultaneous breast pumping is more effective than sequential pumping, producing more milk and draining breasts completely.
The study, performed by the University of Western Australia’s School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, involved a group of 31 mothers of healthy term infants using the same model pump to double and single pump.
For single pumping, the second breast was pumped directly after the first. Each breast was pumped for 15 minutes at the mother’s maximum comfortable vacuum.
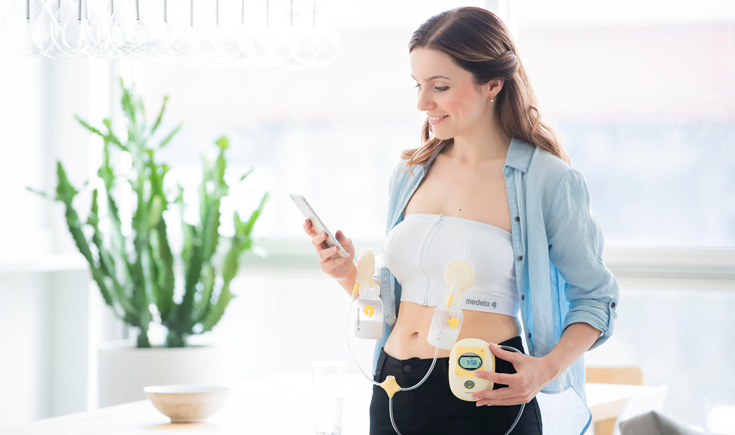
Double pumping saves mothers’ time.
Double pumping means pumping both breasts at the same time, compared to single pumping which is one breast followed by the other breast. During the study, each breast was pumped for exactly 15 minutes.
Therefore, the time spent double pumping was a total of 15 minutes, and the time spent single pumping was 30 minutes.
The results – released by Medela – show that double pumping will obtain on average 18% more milk volume than single pumping.
In addition, after double pumping for 15 minutes, the fat content of the total amount of pumped milk is 8.3%.
This is considerably higher than the 7.3% measured during single pumping.
This is significant for two reasons;
- Firstly, during breastfeeding/pumping, milk changes from low fat (the first milk) to high fat (the last milk). When we have milk with a higher fat content, it means that the breast has been drained better which is the case when double pumping.
- Secondly, milk of a higher fat content can be very important for babies with growth issues such as premature babies, who can only take very small volumes of milk in their small stomachs. For these babies, making sure that the milk is of high caloric value is very important. This is also the case for older babies who may not be gaining weight as well as clinicians would like.
How does this happen?
According to the study, during double pumping there is an additional milk ejection compared to single pumping.
This helps in draining the breast resulting in increased milk volume pumped and the removal of more of the fat rich milk remaining in the breast.
A milk ejection occurs when the hormone oxytocin is released. This contracts the myoepithelial cells around the alveoli and pushes milk out toward the nipple. Milk ejections are essential for milk removal and a successful lactation.
So what does this all mean?
It means that double pumping is not only faster, but it is more effective in removing milk.
Double pumping stimulates an additional milk ejection resulting in 18% more milk volume being pumped in this 15 minute pumping time.
Therefore more of the high fat hind milk is removed, leading to better breast drainage and milk of a higher caloric value.
See video demonstration